Electric Car Technology 101: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
In the rapidly evolving world of automotive technology, electric cars have emerged as a symbol of innovation and environmental consciousness. As concerns about climate change and fossil fuel dependency grow, electric vehicles (EVs) offer a promising solution. This guide aims to provide beginners with a comprehensive understanding of electric car technology, exploring its history, how it works, and its benefits. Whether you’re considering purchasing an EV or simply curious about the technology, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need.
The Evolution of Electric Cars
The concept of electric vehicles is not as modern as one might think. In fact, the history of electric cars dates back to the early 19th century. The first crude electric vehicle was introduced in the 1830s, but it wasn’t until the late 1800s that electric cars started gaining popularity. By the early 1900s, electric vehicles accounted for a significant portion of all vehicles on the road, particularly in urban areas.
However, the rise of gasoline-powered cars, with their longer range and mass production capabilities, eventually overshadowed electric vehicles. It wasn’t until the late 20th century, amidst growing environmental concerns and advancements in battery technology, that electric cars began to make a comeback.
How Electric Cars Work
Understanding how electric cars work is fundamental to appreciating their advantages. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, electric cars use an electric motor powered by electricity stored in batteries. Here’s a simplified explanation of the main components:
- Electric Motor: Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the car.
- Battery Pack: Stores electrical energy and powers the electric motor.
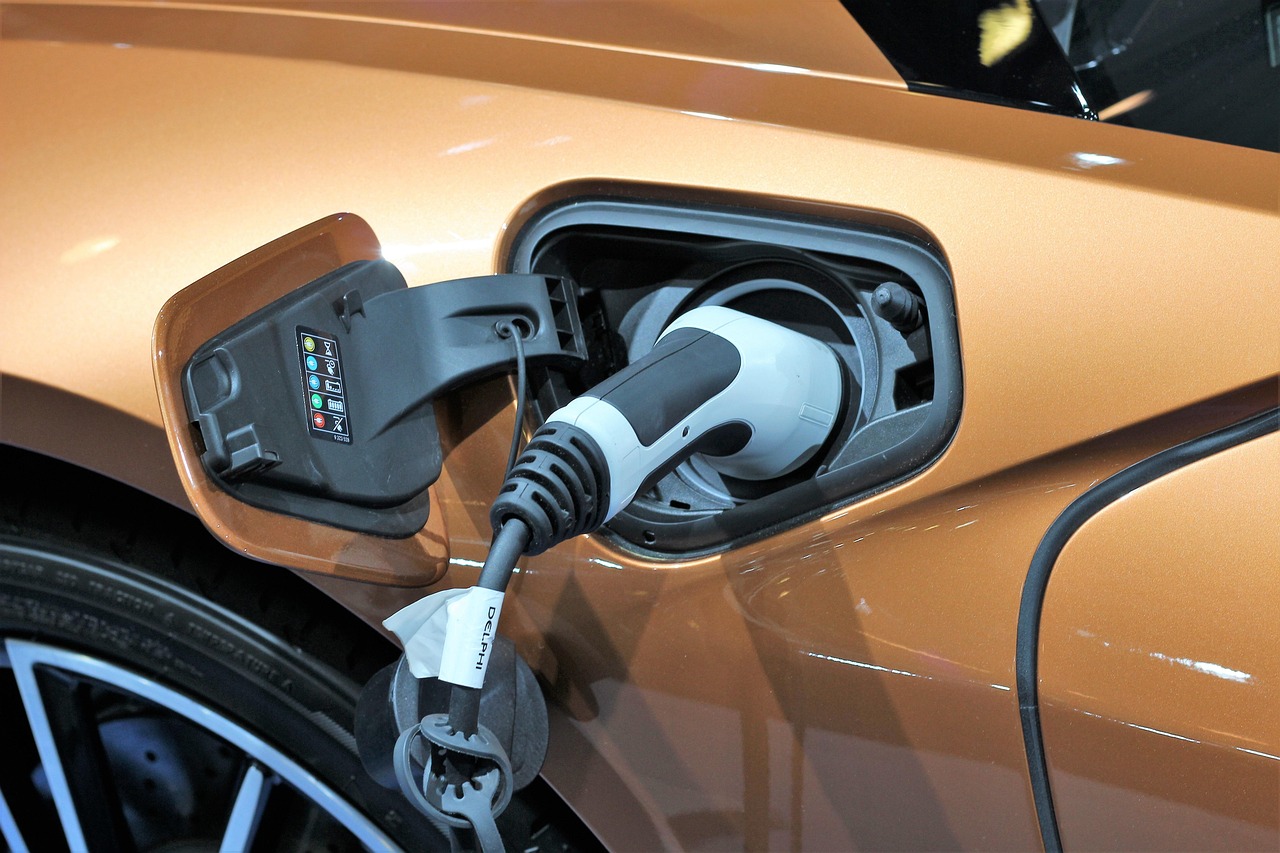
- Charging Port: Connects the car to an external power supply to recharge the battery.
- Inverter: Converts direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) for the electric motor.
- Drivetrain: Transfers power from the motor to the wheels, often more efficiently than in gas-powered vehicles.
The absence of a traditional engine means electric cars are quieter and have fewer moving parts, reducing maintenance needs and increasing reliability. To delve deeper into the mechanics of electric vehicles, consider exploring resources from trusted energy organizations.
Types of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles come in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and advantages:
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): Fully electric cars that rely solely on battery power. Examples include the Tesla Model S and Nissan Leaf.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): Combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor and battery. They can run on electricity for short distances and switch to gasoline for longer trips. Examples include the Chevrolet Volt and Toyota Prius Prime.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): Use a combination of a gasoline engine and an electric motor but don’t plug into an external power source. Examples include the Toyota Prius and Honda Insight.
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs): Generate electricity using hydrogen gas and emit only water vapor. Examples include the Toyota Mirai and Hyundai Nexo.
Each type of electric vehicle offers different benefits and trade-offs, allowing consumers to choose based on their specific needs and environmental goals.
Benefits of Electric Cars
Electric cars offer numerous benefits, making them an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers and tech enthusiasts alike. Here are some key advantages:
Environmental Impact
One of the main reasons people choose electric cars is their reduced environmental impact. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and contributing to cleaner cities. Additionally, as the electric grid becomes greener, the overall carbon footprint of electric cars continues to decrease.
Cost Savings
While the initial purchase price of electric cars can be higher than that of traditional vehicles, the cost of ownership over time tends to be lower. EVs benefit from cheaper fuel costs, reduced maintenance expenses, and potential tax incentives and rebates. Drivers can save significantly on fuel, especially with home charging options.
Performance and Convenience
Electric cars offer impressive performance, with instant torque providing quick acceleration. They are often quieter and smoother to drive than their gasoline counterparts. Additionally, the convenience of charging at home and the growing network of public charging stations make EVs more accessible than ever.
Challenges Facing Electric Cars
Despite their benefits, electric cars face challenges that need addressing to achieve widespread adoption:
Range Anxiety
One of the primary concerns for potential EV buyers is range anxiety—the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station. While advancements in battery technology have significantly increased range, the availability of charging infrastructure remains a critical factor.
Charging Infrastructure
The development of a robust charging network is essential for the mass adoption of electric vehicles. While urban areas are seeing improvements in charging station availability, rural regions may still have limited access. Organizations like International Energy Agency are working towards solutions to expand charging networks worldwide.
Battery Technology
Battery life and disposal are ongoing challenges. Research is underway to improve battery longevity, efficiency, and recycling methods. Significant progress in these areas will enhance the sustainability and appeal of electric cars.
The Future of Electric Car Technology
The future of electric car technology is promising, with continuous advancements on the horizon. Automakers are investing heavily in research and development to create vehicles with longer ranges, faster charging times, and lower costs. Innovations like solid-state batteries and wireless charging could revolutionize the industry.
Furthermore, the integration of electric vehicles with smart grid technology holds potential for optimizing energy use and reducing grid stress. Autonomous driving technology is also likely to complement electric vehicles, offering new levels of convenience and safety.
Takeaways
Electric car technology represents a significant shift in the automotive industry, offering a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to traditional vehicles. While challenges remain, the advantages of electric vehicles are undeniable, and continued innovation promises to overcome existing barriers. For beginners looking to understand this exciting field, grasping the basics of how electric cars work, their benefits, and future potential is essential. As society moves towards a more sustainable future, electric cars are set to play a crucial role.
How to Choose the Right Electric Car
Deciding on the right electric vehicle can be overwhelming given the variety of choices and technological specifications. Here are some key considerations to help you make an informed decision:
Driving Needs and Lifestyle
Consider your daily driving habits. If you typically drive short distances in urban environments, a BEV with a moderate range might suffice. For longer commutes or frequent road trips, a PHEV or a BEV with extended range could be more suitable.
Budget and Incentives
While the upfront cost of an electric car can be higher than that of a traditional car, remember to factor in long-term savings on fuel and maintenance. Be sure to research available tax credits and incentives in your region, as these can significantly offset the purchase price.
Charging Options
Evaluate the availability of charging infrastructure near your home, workplace, and along your usual routes. If home charging is feasible, it provides the convenience of starting each day with a full battery. Otherwise, access to reliable public charging stations will be important.
Battery Life and Warranty
Battery longevity is a crucial aspect of ownership. Most manufacturers offer warranties on their EV batteries, so check the terms and conditions for peace of mind. Consider the manufacturer’s reputation for battery durability and vehicle reliability.
Electric Cars and Sustainable Energy
One of the significant advantages of electric vehicles is their potential to integrate seamlessly with sustainable energy solutions. This synergy can amplify the environmental benefits of EVs, making them even more attractive options for eco-conscious consumers.
Renewable Energy Sources
Charging electric cars with renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or hydroelectric power can drastically reduce their carbon footprint. Homeowners may consider installing solar panels to power their vehicles, aligning with a more sustainable lifestyle.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
V2G technology allows electric vehicles to communicate with the power grid, enabling bidirectional energy flow. This means EVs can store excess energy and return it to the grid during peak demand times, providing stability and reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
Common Misconceptions About Electric Cars
Despite their growing popularity, misconceptions about electric cars persist. Addressing these can help potential buyers make informed decisions:
Limited Range
Many believe that electric cars cannot travel far enough to be practical. However, most modern EVs offer ranges that comfortably cover daily driving needs. With ongoing advancements, some models now offer ranges exceeding 300 miles on a single charge.
Slow Charging Times
Charging an electric vehicle can vary from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the charging station type. Rapid chargers can significantly reduce the charging time, making it feasible to recharge during a short break.
High Costs
While initial costs may be higher, the total cost of ownership for electric vehicles is often lower due to savings on fuel and maintenance. Government incentives can further reduce the purchase price.
The Role of Governments and Policies
Government policies play a crucial role in the adoption and development of electric car technology. Many countries are investing in infrastructure and providing incentives to encourage consumers to switch to electric vehicles.
Infrastructure Development
Investing in charging infrastructure is essential for supporting the growing number of electric vehicles on the road. Governments are collaborating with private companies to expand networks of fast-charging stations, making EVs more convenient for all drivers.
Regulatory Support
Regulations aimed at reducing emissions are encouraging automakers to increase their electric vehicle offerings. Some regions have set ambitious targets to phase out internal combustion engine vehicles entirely, accelerating the shift towards electric mobility.
Financial Incentives
In addition to tax credits, governments may offer rebates, reduced registration fees, and other incentives to make electric vehicles more affordable for consumers. These measures are crucial for increasing EV adoption rates.
Final Thoughts
Electric car technology represents a key component of the broader movement towards sustainable transportation. Understanding the intricacies of how electric vehicles work, their benefits, challenges, and the future trajectory of the industry can empower consumers and enthusiasts to make informed choices. As technology advances and infrastructure improves, electric cars are poised to become the norm rather than the exception. By embracing this technology, we can contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable future for generations to come.